
NASA Webb Pushes Boundaries of Observable Universe Closer to Big Bang
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has topped itself once again, delivering on its promise to push the boundaries of the ...

NASA’s Webb Observes Exoplanet Whose Composition Defies Explanation
Scientists using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have observed a rare type of exoplanet, or planet outside our solar system, whose ...

Webb First to Show 4 Dust Shells ‘Spiraling’ Apep, Limits Long Orbit
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has delivered a first of its kind: a crisp mid-infrared image of a system of ...

NASA’s Webb Explores Largest Star-Forming Cloud in Milky Way
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has revealed a colorful array of massive stars and glowing cosmic dust in the Sagittarius ...

NASA’s Webb Observes Immense Stellar Jet on Outskirts of Our Milky Way
A blowtorch of seething gasses erupting from a volcanically growing monster star has been captured by NASA’s James Webb Space ...
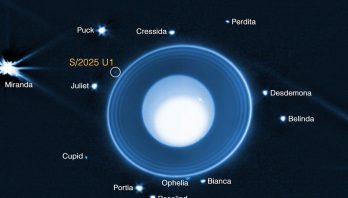
New Moon Discovered Orbiting Uranus Using NASA’s Webb Telescope
Using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, a team led by the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) has identified a previously unknown ...

NASA’s Webb Scratches Beyond Surface of Cat’s Paw for 3rd Anniversary
It’s the cat’s meow! To celebrate its third year of revealing stunning scenes of the cosmos in infrared light, NASA’s ...

Likely Saturn-Mass Planet Imaged by NASA Webb Is Lightest Ever Seen
Astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have captured compelling evidence of a planet with a mass similar to Saturn ...
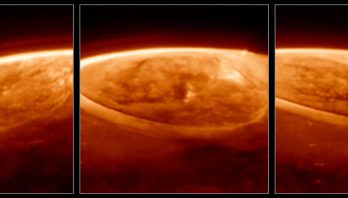
NASA’s Webb Reveals New Details, Mysteries in Jupiter’s Aurora
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured new details of the auroras on our solar system’s largest planet. The dancing ...

NSF NOIRLab Astronomer Discovers Oldest Known Spiral Galaxy in the Universe
An international team led by NSF NOIRLab astronomer Christina Williams has discovered the most distant spiral galaxy known to date ...

With NASA’s Webb, Dying Star’s Energetic Display Comes Into Full Focus
Gas and dust ejected by a dying star at the heart of NGC 1514 came into complete focus thanks to ...
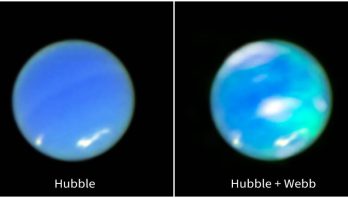
NASA’s Webb Captures Neptune’s Auroras For First Time
For the first time, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured bright auroral activity on Neptune. Auroras occur when energetic ...
