
With NASA’s Webb, Dying Star’s Energetic Display Comes Into Full Focus
Gas and dust ejected by a dying star at the heart of NGC 1514 came into complete focus thanks to ...
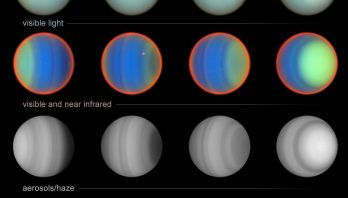
20-Year Hubble Study of Uranus Yields New Atmospheric Insights
The ice-giant planet Uranus, which travels around the Sun tipped on its side, is a weird and mysterious world. Now, ...
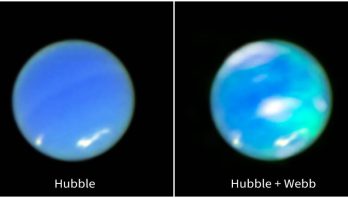
NASA’s Webb Captures Neptune’s Auroras For First Time
For the first time, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured bright auroral activity on Neptune. Auroras occur when energetic ...
Webb Reveals Rapid-Fire Light Show From Milky Way’s Central Black Hole
The supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way appears to be having a party, complete with a ...

Straight Shot: Hubble Investigates Galaxy with Nine Rings
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has captured a cosmic bullseye! The gargantuan galaxy LEDA 1313424 is rippling with nine star-filled rings ...

NASA’s Hubble Traces Hidden History of Andromeda Galaxy
In the years following the launch of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers have tallied over 1 trillion galaxies in the ...

NASA’s Webb Reveals Intricate Layers of Interstellar Dust, Gas
Once upon a time, the core of a massive star collapsed, creating a shockwave that blasted outward, ripping the star ...

Found: First Actively Forming Galaxy as Lightweight as Young Milky Way
For the first time, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has detected and “weighed” a galaxy that not only existed around ...

Hats Off to NASA’s Webb: Sombrero Galaxy Dazzles in New Image
In a new image from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, a galaxy named for its resemblance to a broad-brimmed Mexican ...
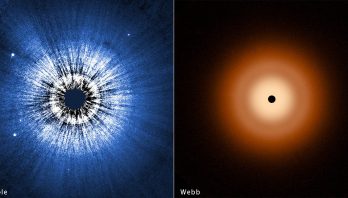
NASA’s Hubble, Webb Probe Surprisingly Smooth Disk Around Vega
A team of astronomers at the University of Arizona, Tucson used NASA's Hubble and James Webb space telescopes for an ...

‘Blood-Soaked’ Eyes: NASA’s Webb, Hubble Examine Galaxy Pair
The gruesome palette of these galaxies is owed to a mix of mid-infrared light from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, ...

NASA’s Hubble Sees a Stellar Volcano
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has provided a dramatic and colorful close-up look at one of the most rambunctious stars in ...
