
Ever-changing Universe Revealed in First Imagery From NSF–DOE Vera C. Rubin Observatory
The NSF-DOE Vera C. Rubin Observatory, a major new scientific facility jointly funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation and ...

Hubble’s Window on the Universe: NASA Celebrates Hubble’s 35th Year in Orbit
In celebration of the Hubble Space Telescope’s 35 years in Earth orbit, NASA is releasing an assortment of compelling images recently ...
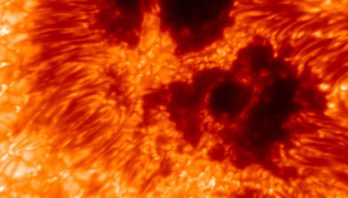
Largest Imaging Spectro-Polarimeter Achieves First Light at the NSF Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope
The U.S. National Science Foundation Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope, the world’s most powerful solar telescope, operated by the NSF ...
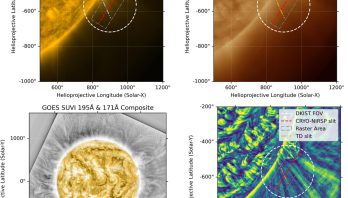
NSF’s Inouye Solar Telescope’s Cryo-NIRSP instrument offers unprecedented look at Alfvén waves
Over the last decade, scientists have confirmed the presence of a an important type of magnetized waves called Alfvén waves ...

NSF NOIRLab Astronomer Discovers Oldest Known Spiral Galaxy in the Universe
An international team led by NSF NOIRLab astronomer Christina Williams has discovered the most distant spiral galaxy known to date ...

With NASA’s Webb, Dying Star’s Energetic Display Comes Into Full Focus
Gas and dust ejected by a dying star at the heart of NGC 1514 came into complete focus thanks to ...

Gemini South Observes Shape and Origin of Near-Earth Asteroid 2024 YR4
Using observations from the Gemini South telescope in Chile, one half of the International Gemini Observatory, partly funded by the ...
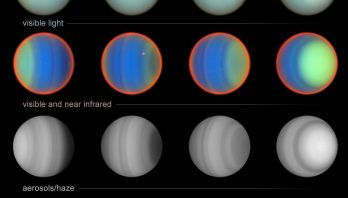
20-Year Hubble Study of Uranus Yields New Atmospheric Insights
The ice-giant planet Uranus, which travels around the Sun tipped on its side, is a weird and mysterious world. Now, ...
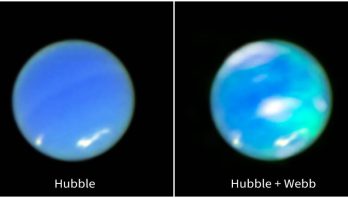
NASA’s Webb Captures Neptune’s Auroras For First Time
For the first time, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured bright auroral activity on Neptune. Auroras occur when energetic ...
Tantalizing Hints That Dark Energy is Evolving — New Results and Data Released by the DESI Project
The DESI collaboration has published a new analysis of dark energy using their first three years of collected data, which ...

Planetary System Found Around Nearest Single Star
Using in part the Gemini North telescope, one half of the International Gemini Observatory, partly funded by the U.S. National ...

DESI Uncovers 300 New Intermediate-Mass Black Holes Plus 2500 New Active Black Holes in Dwarf Galaxies
Within the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument’s early data, scientists have uncovered the largest samples ever of intermediate-mass black holes and ...
