NSO: Study shows temporal patterns of meridional flows are precursors of magnetic activity in solar cycle
By Rudi Komm
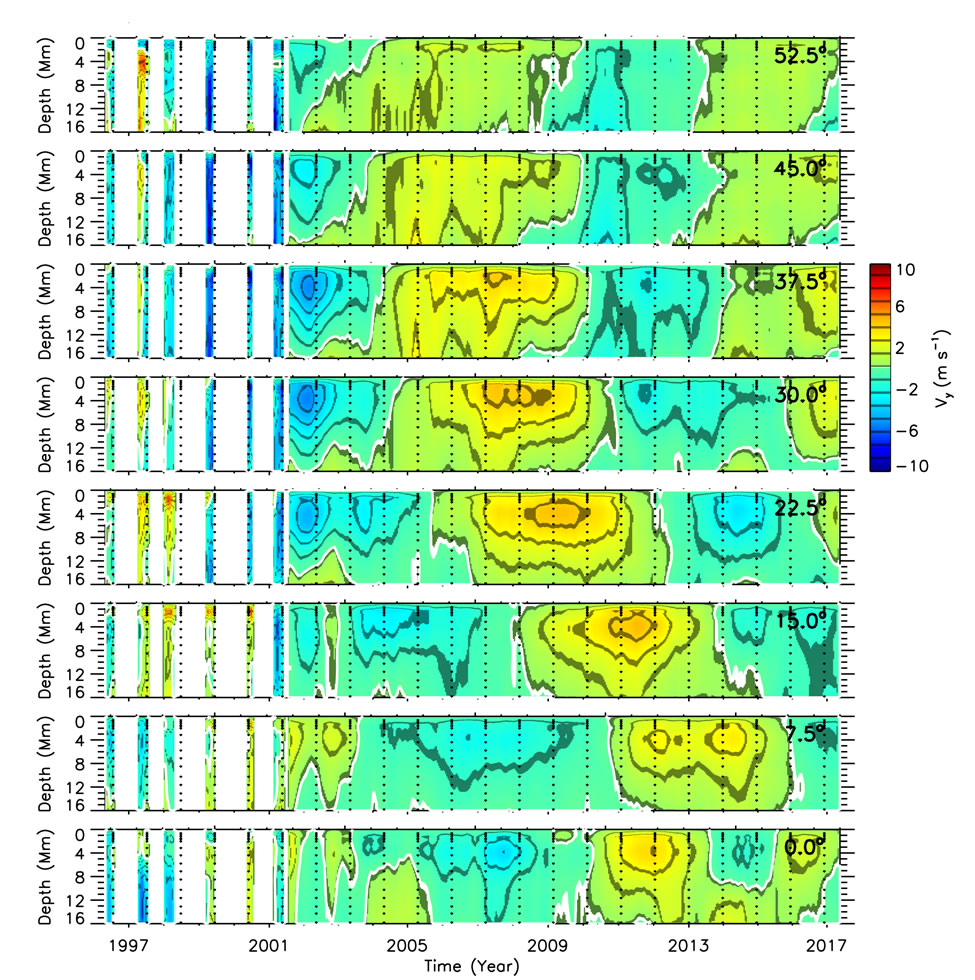
The Sun is a giant ball of heated gases called plasma, more than 1 million km in diameter. The plasma acts like a fluid, resulting in the flow of material throughout the star. The two large-scale flows on the Sun are its rotation about its axis, and the meridional flow. The solar rotation is noticeable, for example, in the way sunspots move across the solar disk.
The meridional flow is much weaker and more elusive than the rotation (about two orders of magnitude) which takes the form of a giant cell flowing from the equator to the poles. It takes long-term observations to accurately measure these large-scale flows. Both flows speed up or slow down depending on the amount of magnetic activity (sunspots, plages, etc.) present on the surface of the Sun and vary with the 11-year solar cycle. These flows are important for the understanding of the solar dynamo, a theory to explain the presence and variation of solar magnetic activity.
