STScI: Hubble Captures Crisp New Portrait of Jupiter’s Storms
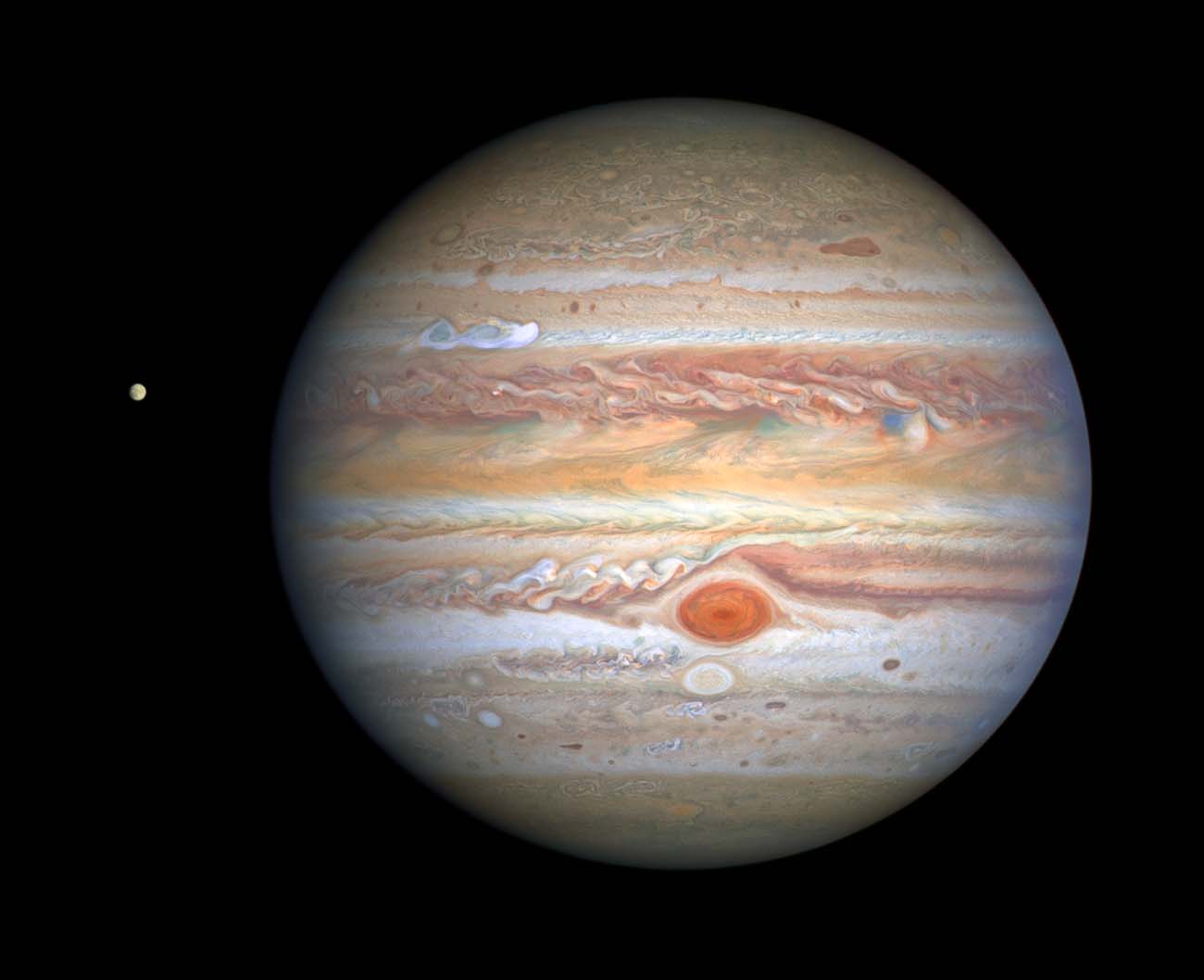
This latest image of Jupiter, taken by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope on August 25, 2020, was captured when the planet was 406 million miles from Earth. Hubble’s sharp view is giving researchers an updated weather report on the monster planet’s turbulent atmosphere, including a remarkable new storm brewing, and a cousin of the Great Red Spot changing color – again. Credits: NASA, ESA, STScI, A. Simon (Goddard Space Flight Center), and M.H. Wong (University of California, Berkeley) and the OPAL team
TURBULENT STORMS RAGE ACROSS THE GIANT PLANET
More massive than all the other planets combined, Jupiter truly is the king of our solar system. The swirling clouds, arranged in colorful, banded structures, change from year to year. The rich colors are produced by trace compounds in Jupiter’s predominantly hydrogen/helium atmosphere. Hurricane-force winds propel these clouds, and upwelling currents are ablaze with lightning bolts far more powerful than those seen on Earth.
The Hubble Space Telescope serves as a “weather satellite” for monitoring Jupiter’s stormy weather. The iconic Great Red Spot, a storm big enough to swallow Earth, shows that it’s shrinking a little in the Hubble images, but it still dominates the entire southern atmosphere, plowing through the clouds like a cargo ship.
Hubble astronomers patiently wait to get close-up snapshots as Earth make its nearest annual approach to Jupiter – an astronomical alignment called an opposition, when Jupiter is on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun. “Closest approach” between the worlds is still on the order of nearly a half billion miles!
